Every Monday we publish education on key business metrics you can use to operate and scale your company. This week we cover three types of profit margin: Gross Margin, Operating Margin, and Net Profit Margin.
Measuring profit margin allows you to assess your business’ performance over time and relative to competitors. Accurate reporting of profit margin is also a typical requirement of banks, investors and other interested parties. Three types of profit margin provide insight into slightly different performance perspectives.
GROSS MARGIN
Gross margin is the first level of profit. Gross margin provides insight into product or service-level profitability. It can help entrepreneurs make decisions around which products or services should be promoted and which may need to be eliminated from their offering. It also provides a baseline from which to identify opportunities for appropriate pricing and cost reduction.
Calculating gross margin starts with computing gross profit. Subtract the costs directly related to producing a product or providing a service from revenue (sales). This dollar amount is then divided by revenue to determine the percent gross profit margin.
Gross Margin = (Sales – Cost of Goods Sold)/Sales
OPERATING MARGIN
Operating margin is the next level of profitability after gross margin. Operating margin provides a view into the performance of a business including its overhead expense.
In order to calculate operating margin, you must first determine operating income. To do so, subtract selling, general and administrative (overhead) expenses from gross profit. This figure is then divided by revenue to determine operating margin.
Operating Margin = (Sales – Cost of Goods Sold – SG&A)/Sales
NET PROFIT MARGIN
Net profit margin, sometimes referred to as net income margin, is the lowest level of profitability. When people refer to a business’ profit margin, it is commonly the net profit margin that they are referring to. It reflects how effective operators are at running their business.
Net income is calculated by subtracting interest, tax, and other expenses from operating profit. Divide net income by revenue to arrive at net profit margin.
Net Profit Margin = (Sales – Cost of Goods Sold – SG&A – Taxes – Interest)/Sales
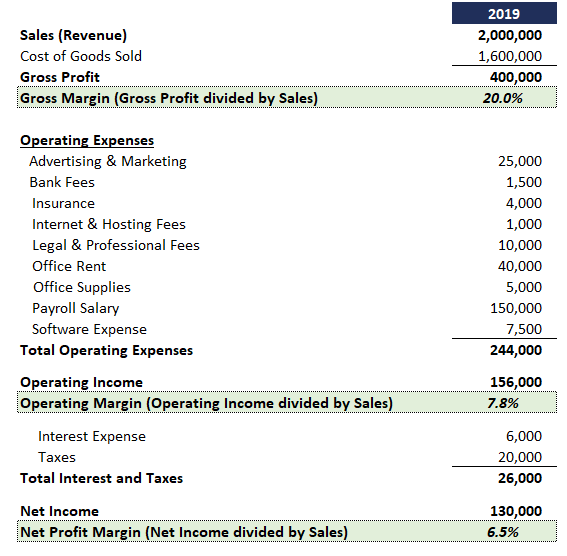
PROFIT MARGIN ILLUSTRATED
See below for a sample financial statement and illustration of the three types of profit margins.
THE BOTTOM LINE
It is difficult to improve what you do not measure. The first step in any business strategy is to determine the important metrics to achieve your goals and measure them. Regularly monitoring profit margin will allow you and others to measure the performance and viability of the business. Use this information to make pricing decisions and manage your business expenses. In doing so, you will maximize profitability, increase business value, and obtain favorable terms when obtaining financing.
If you would like to learn more about other key metrics to help in your decision making or could use a partner to help build a custom KPI Dashboard for your organization, contact us for a free strategy call.